thessaly test meniscus tear|abnormal mcmurray vs thessaly : distribution Thessaly was the most sensitive for medial meniscus tears (76.6%), while McMurray and joint-line tenderness were more specific (81.0%, and 81.0%). The most sensitive test for lateral meniscus tears was combined tests with 68.8% sensitivity, while . Close the door of an Autoclave and connect the outputs of the 12 sensors to the Temperature Data logger. Set the temperature at 121.4°C and Sterilization hold time 30 minutes.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Sterilizer Design It is commonly understood that a “GMP sterilizer” is a unit designed for moist heat sterilization, and built in accordance with current pharmaceutical industry sanitary design .
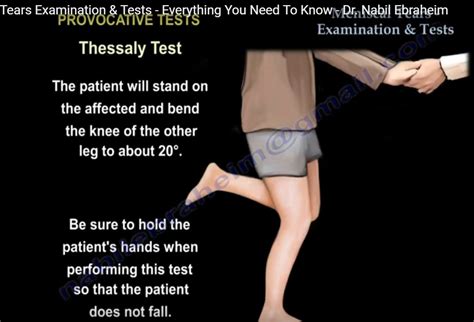
The Thessaly test is a series of knee and leg movements healthcare providers use to diagnose a torn meniscus. It’s an in-office physical exam, which means your provider can perform it without any special equipment or a separate appointment.
This is a clinical screening tool for meniscal tears/ lesions. Patients with suspected meniscal tears experience medial or lateral joint-line discomfort and may have a sense of locking or catching. A systematic review and meta-analysis of studies available through the end of 2014 2 concluded that the Thessaly test has similar, and perhaps slightly superior, accuracy when compared to the.
The Thessaly test has been described as the most accurate test for meniscus lesions by Karachalios et al. (2005). However, there has been new research by Goosens et al. (2015) with a higher quality that states that the sensitivity is as low as 64% and the specificity is as low as 53%.Thessaly was the most sensitive for medial meniscus tears (76.6%), while McMurray and joint-line tenderness were more specific (81.0%, and 81.0%). The most sensitive test for lateral meniscus tears was combined tests with 68.8% sensitivity, while .
The Thessaly Test is used in patients who have a suspected meniscal injury. A positive test is joint line discomfort or a sense of locking or catching. This test should only be performed 4 weeks or more after initial injury as acutely injured .The Thessaly Test (or Thesally’s Test) is a test for detecting meniscal tears/lesions of the knee. Involved Structures. medial meniscus of the knee; lateral meniscus of the knee; Starting Position. The test is performed with the patient in standing with full weight bearing on the side to be tested. The foot should be flat on the floor. Thessaly test. standing at 20 degrees of knee flexion on the affected limb, the patient twists with knee external and internal rotation with positive test being discomfort or clicking. McMurray's test. flex the knee and place a hand on medial side of knee, externally rotate the leg and bring the knee into extension.The Thessaly test is used to assess the integrity of the medial and lateral meniscus, specifically testing meniscal tears. See how to do the thessaly test.
The Thessaly test is a valid and reproducible physical examination technique for predicting meniscal tears. The Thessaly test shows promise as an easily performed maneuver that may have better diagnostic accuracy than traditional tests.
The Thessaly test is a series of knee and leg movements healthcare providers use to diagnose a torn meniscus. It’s an in-office physical exam, which means your provider can perform it without any special equipment or a separate appointment.This is a clinical screening tool for meniscal tears/ lesions. Patients with suspected meniscal tears experience medial or lateral joint-line discomfort and may have a sense of locking or catching. A systematic review and meta-analysis of studies available through the end of 2014 2 concluded that the Thessaly test has similar, and perhaps slightly superior, accuracy when compared to the.
The Thessaly test has been described as the most accurate test for meniscus lesions by Karachalios et al. (2005). However, there has been new research by Goosens et al. (2015) with a higher quality that states that the sensitivity is as low as 64% and the specificity is as low as 53%.
Thessaly was the most sensitive for medial meniscus tears (76.6%), while McMurray and joint-line tenderness were more specific (81.0%, and 81.0%). The most sensitive test for lateral meniscus tears was combined tests with 68.8% sensitivity, while . The Thessaly Test is used in patients who have a suspected meniscal injury. A positive test is joint line discomfort or a sense of locking or catching. This test should only be performed 4 weeks or more after initial injury as acutely injured .The Thessaly Test (or Thesally’s Test) is a test for detecting meniscal tears/lesions of the knee. Involved Structures. medial meniscus of the knee; lateral meniscus of the knee; Starting Position. The test is performed with the patient in standing with full weight bearing on the side to be tested. The foot should be flat on the floor. Thessaly test. standing at 20 degrees of knee flexion on the affected limb, the patient twists with knee external and internal rotation with positive test being discomfort or clicking. McMurray's test. flex the knee and place a hand on medial side of knee, externally rotate the leg and bring the knee into extension.
The Thessaly test is used to assess the integrity of the medial and lateral meniscus, specifically testing meniscal tears. See how to do the thessaly test.
john morris scientific pipette calibration
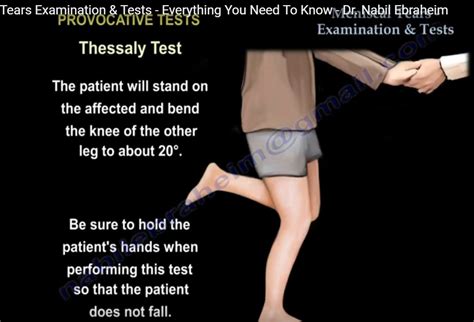
thessaly test for meniscal injury
Autoclaving is the simplest sterilization method if all pipette parts tolerate extreme heat. Pipettes should be autoclaved according to the manufacturer's instructions. To achieve sterility, a holding time of at least 20 minutes at .
thessaly test meniscus tear|abnormal mcmurray vs thessaly